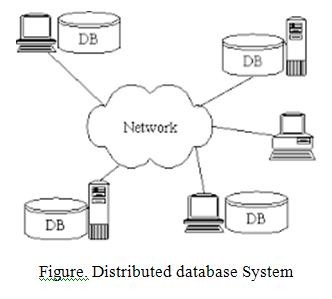
A distributed database management system (D–DBMS) is the software that manages the DDB and provides an access mechanism that makes this distribution transparent to the users. It consists of a single logical database that is split into a number of fragments. Each fragment is stored on one or more computers under the control of a separate DBMS, with the computers connected by a communications network.
Each site is capable of independently processing user requests that require access to local data and is also capable of processing data stored on other computers in the network. Users access the distributed database via applications. Applications are classified as those that do not require data from other sites (local Applications) and those that do require data from other sites (global applications). We require a DDBMS to have at least one global application.
Distributed Database Example (Banking Example)
Using distributed database technology, a bank may implement its database system on a number of separate computer systems rather than a single, centralized mainframe. The computer systems may be located at each local branch office: for example, a new road branch, kalimati branch, Kirtipur branch, etc. A network linking the computer will enable the branches to communicate with each other, and DDBMS will enable them to access data stored at another branch office. Thus a client living in Kirtipur can also check his/her account during the stay in a new road or Kalimati.





0 Comments